The human skeleton of an adult consists of around 206 to 213 bones, and there are 300 bones in children, depending on the counting of the sternum. It is composed of 300 bones at birth but later decreases to 80 bones in the axial skeleton and 126 bones in the appendicular skeleton. Many small accessory bones, such as some sesamoid bones, are not included in this count. There are 20 major bones.
Bones
The axial skeleton, comprising the spine, chest, and head, contains 80 bones, and the appendicular skeleton, comprising the arms and legs, including the shoulder and pelvic girdles, contains 126 bones, bringing the total for the entire skeleton to 206 bones.
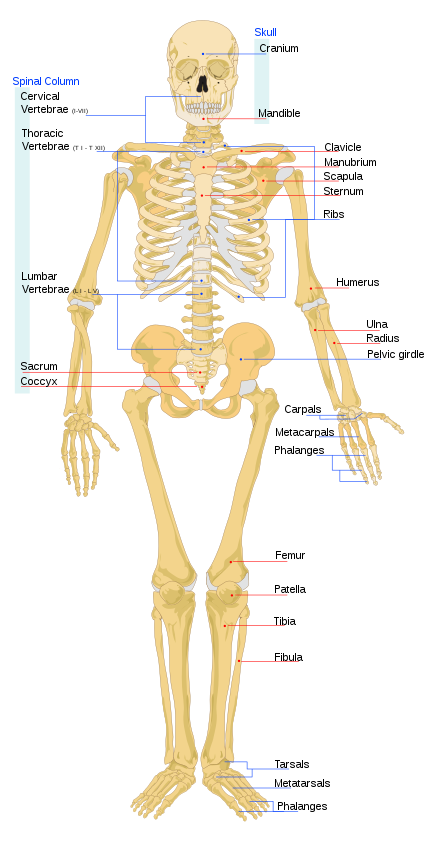
Spine (vertebral column)
A fully grown adult features 26 bones in the spine, whereas a child can have 34.
Cervical vertebrae (7 bones), Thoracic vertebrae (12 bones), Lumbar vertebrae (5 bones), Sacrum (5 bones at birth, fused into one after adolescence), Coccygeal vertebrae/Cordal (set of 4 bones at birth; some or all fuse together, but there seems to be a disagreement between researchers as to what the most common number should be. Some say the most common is 1, others say 2 or 3, with 4 being the least likely.
Chest (thorax)
There are usually 25 bones in the chest but sometimes there can be additional cervical ribs in men. Cervical ribs occur naturally in other animals such as reptiles.
Sternum (1 or 3), Ribs (24, in 12 pairs), and Cervical ribs are extra ribs that occur in some men.
Skull
There are 22 bones in the skull. Including the bones of the middle ear and the hyoid bone, the head contains 29 bones.
Cranial bones (8): Occipital bone, Parietal bones (2), Frontal bone, Temporal bones (2), Sphenoid bone (sometimes counted as facial), and Ethmoid bone (sometimes counted as facial)
Facial bones (15): Nasal bones (2), Maxillae (upper jaw) (2), Lacrimal bone (2), Zygomatic bone (cheekbones) (2), Palatine bone (2), Inferior nasal concha (2), Vomer (1), Hyoid bone (1), and Mandible (1)
Middle ears (6 bones in total, 3 on each side): Malleus (2), Incus (2), and Stapes (2)
Arm
There are a total of 64 bones in the arms, 32 in each arm
Upper arm bones (6 bones in total; 3 on each side), Humerus (2), Pectoral girdle (shoulder), Scapula (2), and Clavicles (2),
Lower arm bones (4 bones in total, 2 on each side) left bone, Ulna (2), and Radius (2),
Hand (54 bones in total; 27 in each hand), Carpals, Scaphoid bone (2), Lunate bone (2), Triquetral bone (2), Pisiform bone (2), Trapezium (2), Trapezoid bone (2), Capitate bone (2), Hamate bone (2). Metacarpals (10 bones in total; 5 on each side). Phalanges of the hand: Proximal phalanges (10 bones in total; 5 on each side), Intermediate phalanges (8 bones in total; 4 on each side), and Distal phalanges (10 bones in total; 5 on each side)
Pelvis (pelvic girdle)
The pelvis (or hip bone) is made up of three regions that have fused to form 2 coxal bones. They are: ilium, ischium, and pubis. The sacrum and the coccyx attach to the two hip bones to form the pelvis but are more important to the spinal column, where they are counted.
Leg:
There are a total of 60 bones in the legs.
Femur (2 bones), Patella or kneecap (2 bones), Tibia (2 bones), Fibula (2 bones). Foot (52 bones in total, 26 per foot): Calcaneus or heel bone (2 bones), Talus (2 bones), Navicular bone (2 bones), Medial cuneiform bone (2 bones), Intermediate cuneiform bone (2 bones), Lateral cuneiform bone (2 bones), Cuboid bone (2 bones), Metatarsals (10 bones), Proximal phalanges (10 bones), Intermediate phalanges ( 8 bones), and Distal phalanges (10 bones)
More from Bright Star